使用Spring进行单元测试(上)
作者:网络转载 发布时间:[ 2013/6/5 11:10:53 ] 推荐标签:
另外,在这个测试类中,我们还不能使用 Spring 的依赖注入特性。一切都靠手工编码实现。好,那么我们看看 Spring test 框架能做到什么。
首先我们修改一下 Spring 的 XML 配置文件,删除 <context:annotation-config/> 行,其他不变。
清单 6. Spring-db1.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.Springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.Springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.Springframework.org/schema/beans/Spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="datasource"
>
<property name="driverClassName" value="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:hsqldb:hsql://localhost" />
<property name="username" value="sa"/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager"
>
<property name="dataSource" ref="datasource"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="initer" init-method="init">
</bean>
<bean id="accountDao" depends-on="initer">
<property name="dataSource" ref="datasource"/>
</bean>
<bean id="accountService">
</bean>
</beans>
其中的 transactionManager 是 Spring test 框架用来做事务管理的管理器。
清单 7. AccountServiceTest1.Java
package service;
import static org.Junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.Junit.Test;
import org.Junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.Springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.Springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.Springframework.test.context.Junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.Springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import domain.Account;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("/config/Spring-db1.xml")
@Transactional
public class AccountServiceTest1 {
@Autowired
private AccountService service;
@Test
public void testGetAcccountById() {
Account acct = Account.getAccount(1, "user01", 18, "M");
service.insertIfNotExist(acct);
Account acct2 = service.getAccountById(1);
assertEquals(acct,acct2);
}
}
对这个类解释一下:
● @RunWith 注释标签是 Junit 提供的,用来说明此测试类的运行者,这里用了 SpringJUnit4ClassRunner,这个类是一个针对 Junit 运行环境的自定义扩展,用来标准化在 Spring 环境中 Junit4.5 的测试用例,例如支持的注释标签的标准化
● @ContextConfiguration 注释标签是 Spring test context 提供的,用来指定 Spring 配置信息的来源,支持指定 XML 文件位置或者 Spring 配置类名,这里我们指定 classpath 下的 /config/Spring-db1.xml 为配置文件的位置
● @Transactional 注释标签是表明此测试类的事务启用,这样所有的测试方案都会自动的 rollback,即您不用自己清除自己所做的任何对数据库的变更了
● @Autowired 体现了我们的测试类也是在 Spring 的容器中管理的,他可以获取容器的 bean 的注入,您不用自己手工获取要测试的 bean 实例了
● testGetAccountById 是我们的测试用例:注意和上面的 AccountServiceOldTest 中相同的测试方法的对比,这里我们不用再 try-catch-finally 了,事务管理自动运行,当我们执行完成后,所有相关变更会被自动清除
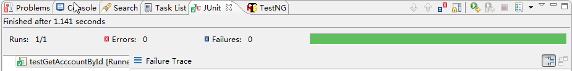
执行结果
在 Eclipse 的 Junit 视图中,我们可以看到如下的结果:
图 3. 执行结果
小结
如果您希望在 Spring 环境中进行单元测试,那么可以做如下配置:
● 继续使用 Junit4 测试框架,包括其 @Test 注释标签和相关的类和方法的定义,这些都不用变
● 您需要通过 @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) 来启动 Spring 对测试类的支持
● 您需要通过 @ContextConfiguration 注释标签来指定 Spring 配置文件或者配置类的位置
● 您需要通过 @Transactional 来启用自动的事务管理
● 您可以使用 @Autowired 自动织入 Spring 的 bean 用来测试
另外您不再需要:
● 手工加载 Spring 的配置文件
● 手工清理数据库的每次变更
● 手工获取 application context 然后获取 bean 实例















 sales@spasvo.com
sales@spasvo.com